Public Health
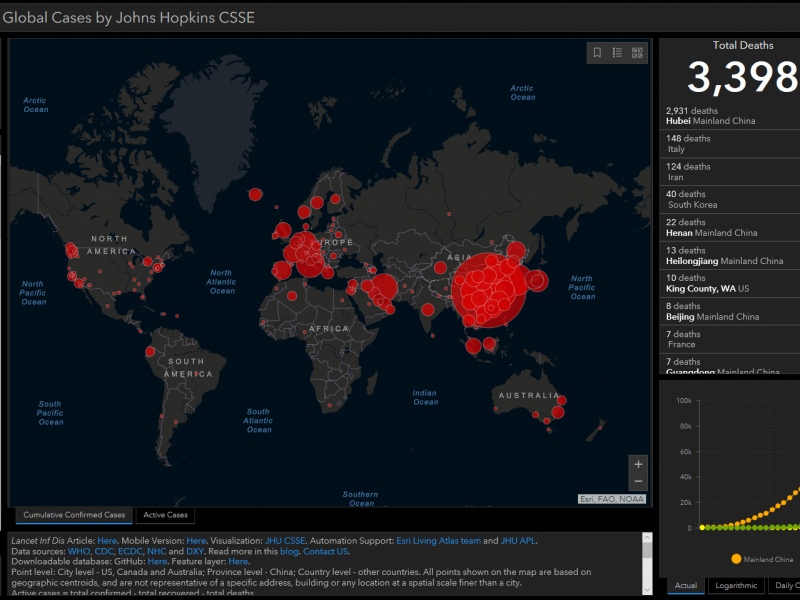
COVID-19
We developed and manage an interactive dashboard mapping the COVID-19 pandemic in real-time, and have conducted various modeling studies to aid public health policy makers in their decision making. This work is sponsored by NSF, NIH, NASA and JHU.

Measles
Our work on measles focuses on the development of a risk assessment framework to forecast likely measles hotspots, by taking into account local vaccination rates, travel patterns, and real-time status of measles outbreaks around the world.

Inferring the risk factors that drive outbreak dynamics
We exploit available epidemiological data, travel data, land use patterns, climate data, sociodemographic data, and ecological models within statistical and optimization-based frameworks to infer the most significant risk factors that contribute to infectious disease dynamics.

Optimizing Resource Allocation for Outbreak Control
We develop decision support frameworks, specifically models which can provide robust outbreak control policies, for designing appropriate and targeted control measures to mitigate the risk posed by infectious disease. The research requires solving a constrained resource allocation problem, while concurrently accounting for stochastic outbreak dynamics.
Predicting the spread of infectious diseases
We utilize available epidemiological data, travel data, land use patterns, climate data, sociodemographic data, and ecological models within statistical and machine learning frameworks to predict infectious disease risk at various spatial and temporal scales. Applications include measles, Zika, dengue, MERS-CoV and influenza.

Spatial-temporal modelling of Avian Influenza
We have conducted various comparative analysis to elucidate the risk factors and spreading dynamics of avian influenza, including H7N9 and H5N1 in China, and various H5 subtypes in the U.S. The resulting risk modelling frameworks reveal the regions at highest risk of transmission, as well as the underlying environmental and human factors that contribute most substantially to the spreading risk.

Public Health Policy
We synthesize our findings from various modelling studies on infectious disease risk, ranging from MERS-CoV to Zika to Measles, to aid public health policy makers in their decision making.

Inferring Contagion Patterns in Networks
We infer the most likely transmission paths of infectious disease in social-contact networks, where a population of connected individuals is represented using nodes and links. The problem is formulated as a mathematical program, and solved using a novel heuristic method which seeks to find the set of maximum likelihood spanning trees.

Modeling bio-security risk in public transit systems
We utilize network analysis tools to represent the interaction of individuals using a city’s public transit system to evaluate a range of infectious disease threats. The models arevused to identify critical and vulnerable components of the system (e.g., super spreading vehicle-trips), which can be prioritized for monitoring and control during an emerging outbreak.