Public Health
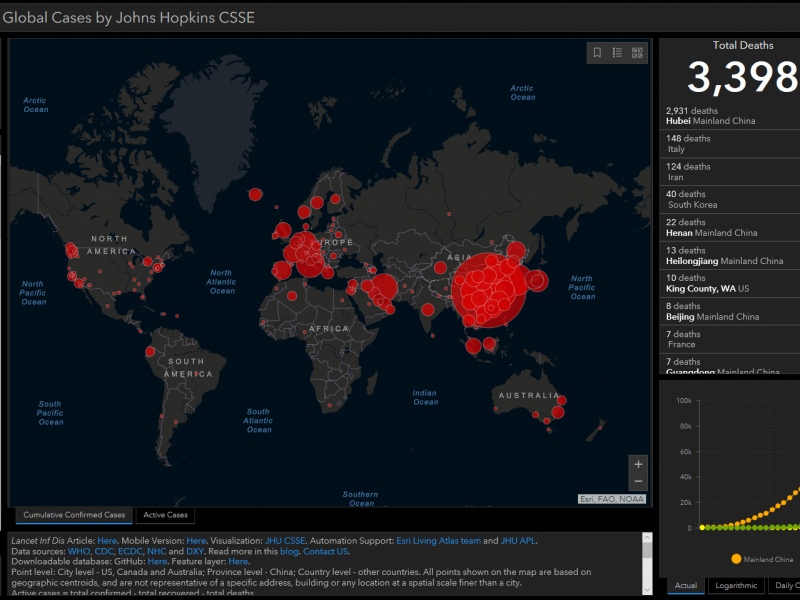
COVID-19
We developed and manage an interactive dashboard mapping the COVID-19 pandemic in real-time, and have conducted various modeling studies to aid public health policy makers in their decision making. This work is sponsored by NSF, NIH, NASA and JHU.

Measles
Our work on measles focuses on the development of a risk assessment framework to forecast likely measles hotspots, by taking into account local vaccination rates, travel patterns, and real-time status of measles outbreaks around the world.

Inferring the risk factors that drive outbreak dynamics
We exploit available epidemiological data, travel data, land use patterns, climate data, sociodemographic data, and ecological models within statistical and optimization-based frameworks to infer the most significant risk factors that contribute to infectious disease dynamics.

Optimizing Resource Allocation for Outbreak Control
We develop decision support frameworks, specifically models which can provide robust outbreak control policies, for designing appropriate and targeted control measures to mitigate the risk posed by infectious disease. The research requires solving a constrained resource allocation problem, while concurrently accounting for stochastic outbreak dynamics.
Predicting the spread of infectious diseases
We utilize available epidemiological data, travel data, land use patterns, climate data, sociodemographic data, and ecological models within statistical and machine learning frameworks to predict infectious disease risk at various spatial and temporal scales. Applications include measles, Zika, dengue, MERS-CoV and influenza.

Spatial-temporal modelling of Avian Influenza
We have conducted various comparative analysis to elucidate the risk factors and spreading dynamics of avian influenza, including H7N9 and H5N1 in China, and various H5 subtypes in the U.S. The resulting risk modelling frameworks reveal the regions at highest risk of transmission, as well as the underlying environmental and human factors that contribute most substantially to the spreading risk.

Public Health Policy
We synthesize our findings from various modelling studies on infectious disease risk, ranging from MERS-CoV to Zika to Measles, to aid public health policy makers in their decision making.

Inferring Contagion Patterns in Networks
We infer the most likely transmission paths of infectious disease in social-contact networks, where a population of connected individuals is represented using nodes and links. The problem is formulated as a mathematical program, and solved using a novel heuristic method which seeks to find the set of maximum likelihood spanning trees.

Modeling bio-security risk in public transit systems
We utilize network analysis tools to represent the interaction of individuals using a city’s public transit system to evaluate a range of infectious disease threats. The models arevused to identify critical and vulnerable components of the system (e.g., super spreading vehicle-trips), which can be prioritized for monitoring and control during an emerging outbreak.
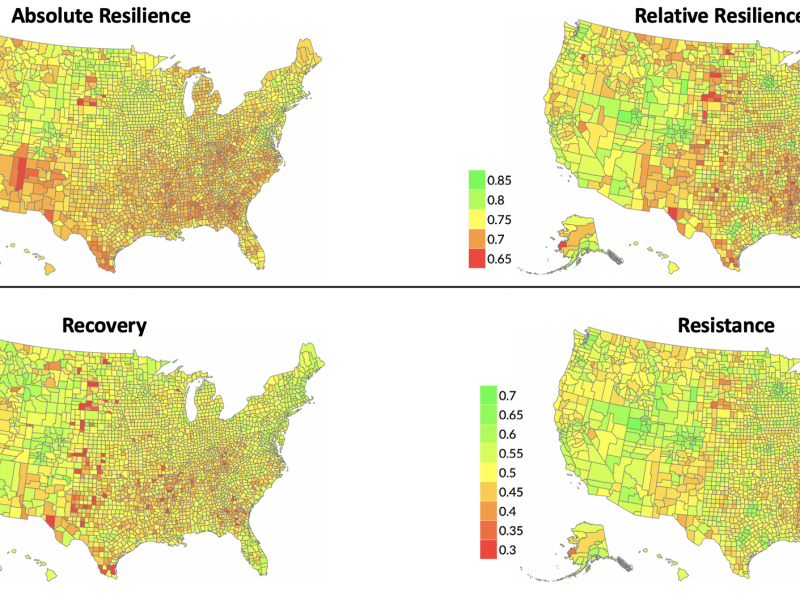
COPEWELL (Composite of Post-Event Well-being)
Policymakers and practitioners need to assess community resilience in disasters. Models of community function and resilience after a disaster can be modeled with system dynamic models. The model outputs the time course of community functioning before, during, and after a disaster. This information can be used to calculate resistance, recovery, and resilience in US counties. Models like this can be applied to other public health studies.
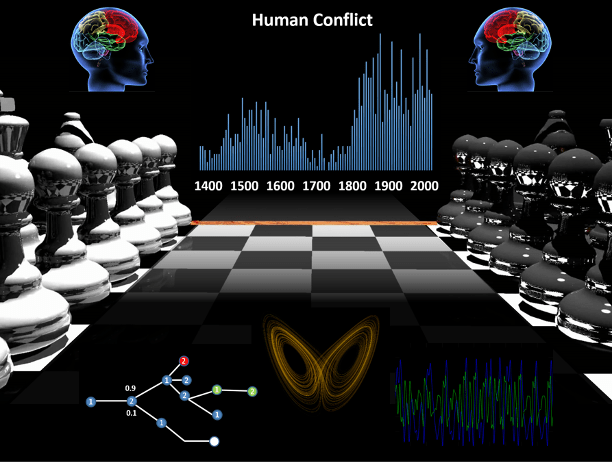
Nuclear Deterrence
Research on the effectiveness of nuclear weapons in preventing conflict can help to inform strategic decisions in the defense community in order to enhance National Security. Investigating nuclear deterrence and human conflict from a systems science perspective, using methods such as complexity theory, nonlinear dynamics, networks, advanced statistics, and agent-based modeling, provides a unique approach.
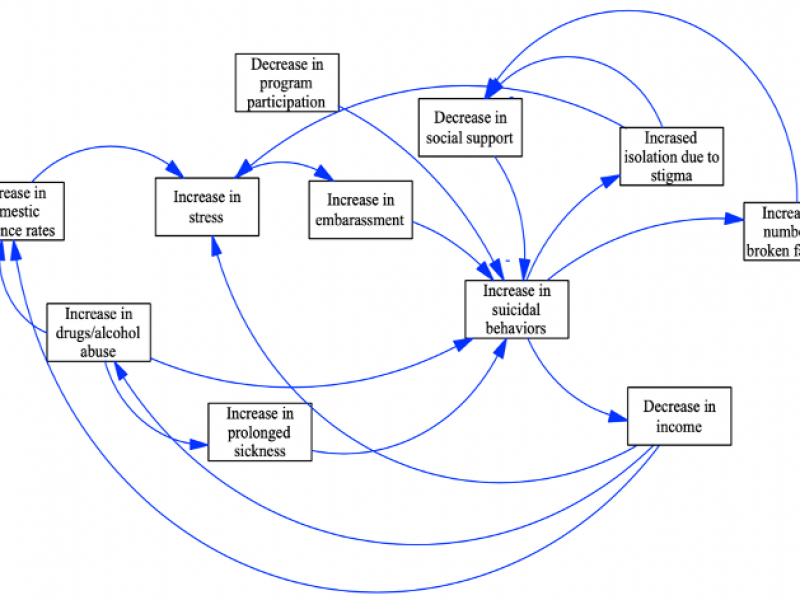
Suicide Prevention in a Thai Refugee Camps
There is currently little epidemiologic research on suicidal behaviors among displaced populations. This study aims to inform suicide prevention strategies in refugee camps in Northwestern Thailand. Causes, consequences, and interventions to prevent suicidal behaviors among refugees can be modeled using a Community Based System Dynamics (CBSD) approach. Participatory system dynamics modeling allows for local stakeholders to be involved, providing a more in depth understanding of factors that contribute to suicide attempts. This helps to study suicide prevention within the context of displacement and to optimize prevention efforts.
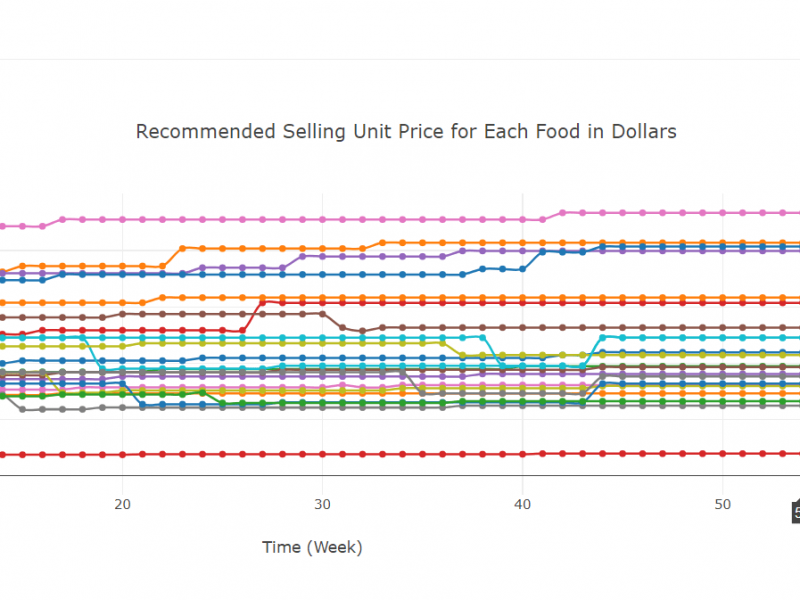
Staple Food Ordinance
In some areas of Baltimore, particularly low-income communities, corner stores are the main source of food. Using a System Dynamics modeling method, a web-based application was created. This research simplifies complex models so they can be used by those who need them, allowing for more meaningful and helpful results. The results can help the government to establish a new food ordinance which would require corner stores to keep certain foods in stock. The model informs what amounts of different kinds of foods should be put in stock.
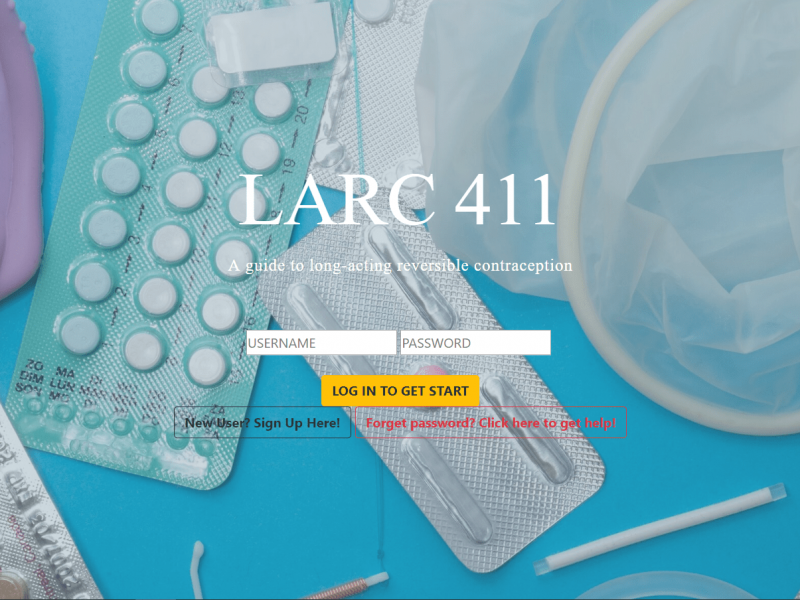
Long-acting Reversible Contraception (LARC) Web Application
In this study, a web app was created that helps new and potential long-acting reversible contraception (LARC) users understand different types of LARCs and answer their questions. The web app utilizes a neuro-linguistic programming (NLP) algorithm to build an interactive application that is easy to use.
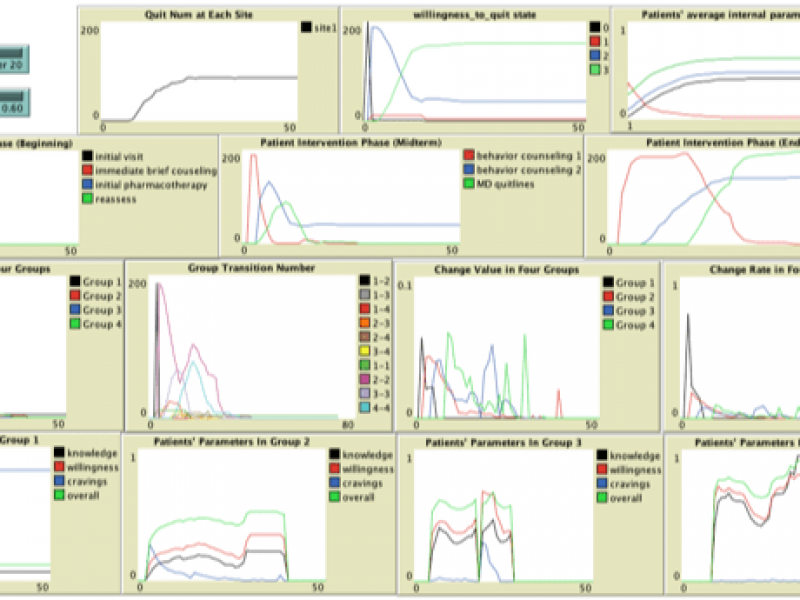
TOBACCO SMOKING CESSATION TREATMENT FOR PEOPLE WITH SERIOUS MENTAL ILLNESS
This project uses agent-based models to study smoking cessation treatment for people in community mental health clinics, allowing for a study on how these interventions can be expanded. The modeling allows researchers to study the underlying rules and mechanisms among people’s interactions to find patterns in the systems. Models like this can be applied to other public health topics such as weight loss intervention and hypertension control.